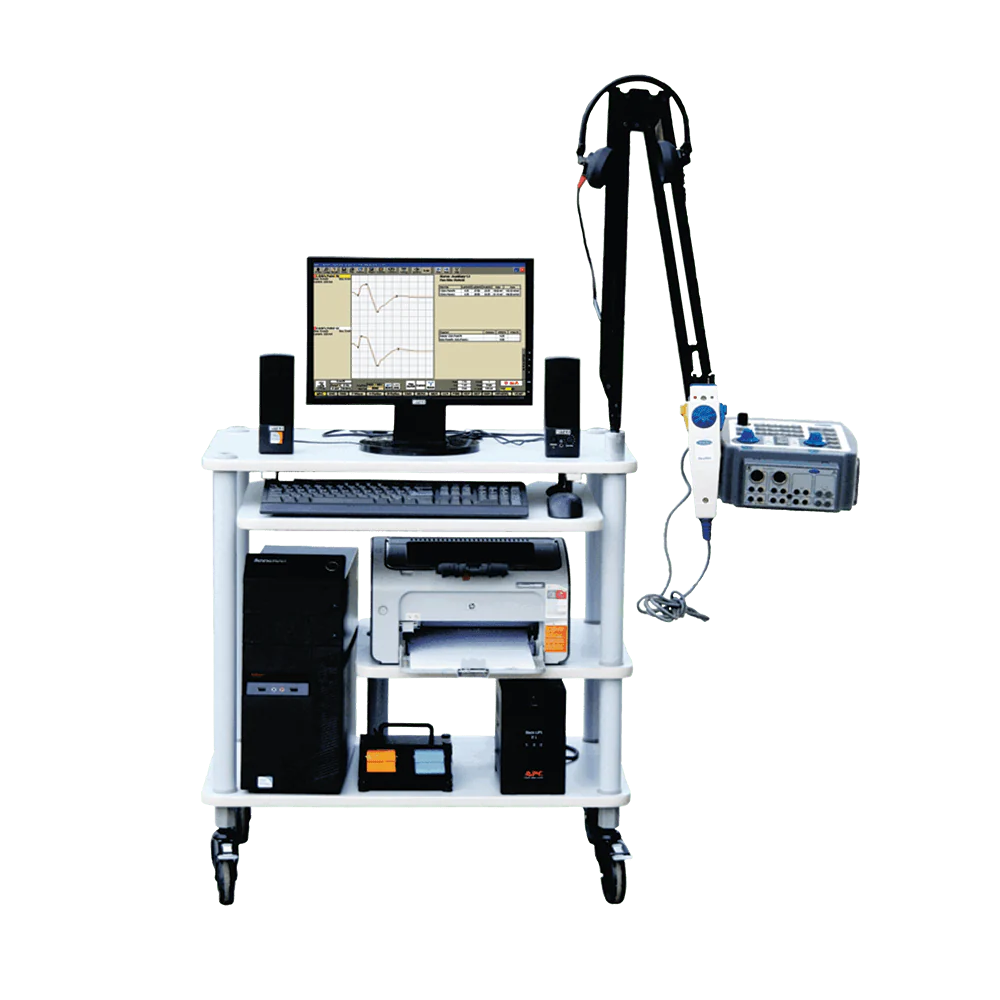


EMG/NCS (Electromyography/Nerve Conduction Study)
EMG/NCS (Electromyography/Nerve Conduction Study) is a diagnostic test used to evaluate the health of your muscles and the nerves controlling them. It helps identify nerve damage, muscle disorders, and conditions like neuropathy or radiculopathy. NCS measures how quickly electrical signals move through your nerves, while EMG checks the electrical activity in muscles. The test is crucial for diagnosing unexplained muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling. It is safe, minimally invasive, and provides valuable insights for accurate treatment planning.
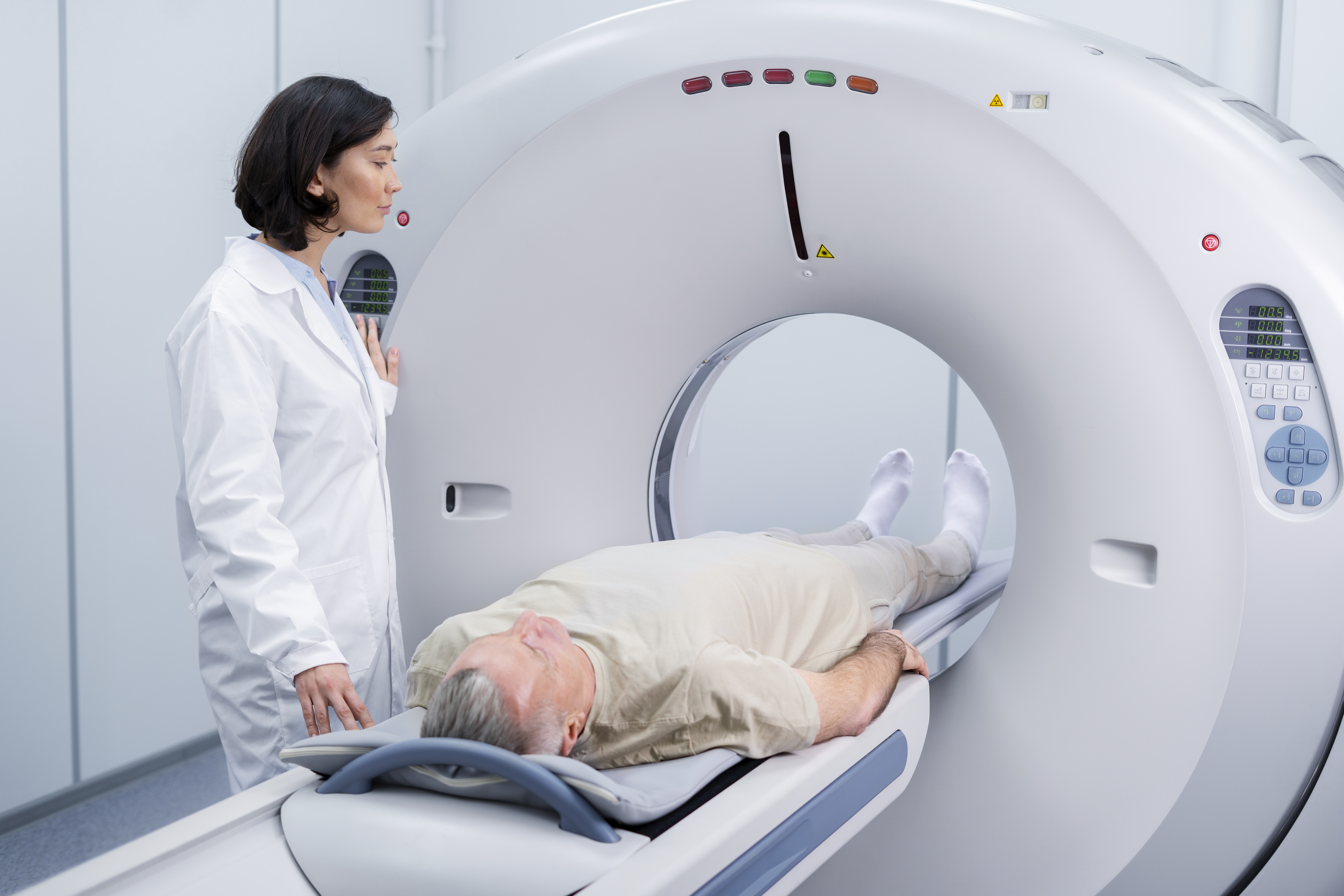
CT Scan
A CT Scan (Computed Tomography Scan) is a powerful imaging test that provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It helps detect internal injuries, tumors, infections, and other abnormalities with high precision. CT scans are commonly used for brain, chest, abdomen, and bone evaluations. The procedure is quick, painless, and non-invasive. With advanced imaging technology, CT scans offer accurate diagnosis and guide effective treatment plans.

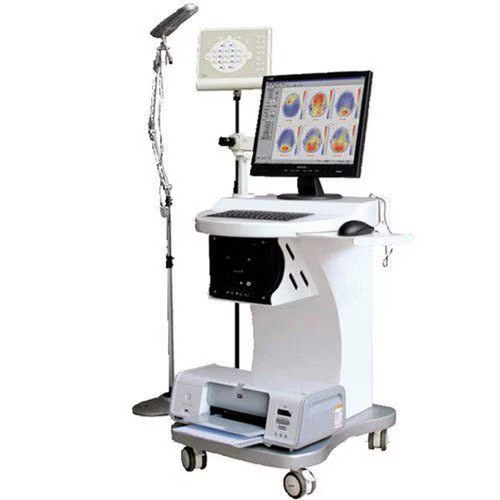

EEG (Electroencephalogram)
An EEG (Electroencephalogram) is a diagnostic test that measures electrical activity in the brain. It is commonly used to detect and monitor conditions like epilepsy, seizure disorders, sleep disorders, head injuries, encephalitis, and brain dysfunction. During the test, small electrodes are placed on the scalp to record brain wave patterns. EEG is non-invasive, safe, and painless, making it suitable for patients of all ages. It helps neurologists identify abnormal brain activity and guide appropriate treatment strategies. EEGs can also be used to monitor brain function during surgery or after a coma. This test plays a key role in understanding unexplained neurological symptoms like fainting, confusion, or memory loss.
